A new paradigm is reshaping cloud infrastructure: neoclouds. These AI-first next-gen cloud providers are building GPU-dense platforms designed for the unrelenting scale and performance demands of modern machine learning. Unlike traditional cloud providers retrofitting existing infrastructure, neoclouds are purpose-building AI-native fabrics from the ground up—where every GPU cycle counts and every packet matters.
In these AI-native environments, the network is no longer a passive conduit. It’s the synchronizing force that keeps colossal clusters of GPUs running at full throttle, every second of the day. Achieving this requires more than just bandwidth: it demands deterministic, lossless operation, deep observability, and the agility to evolve as AI workloads and architectures shift.
The Neocloud blueprint: Open, scalable, and AI-optimized with Cisco 8000
This is where the Cisco 8000 Series with SONiC steps in—not as a traditional switch, but as the intelligent backbone for neoclouds. Designed for a disaggregated, open networking approach, the Cisco 8000 Series with SONiC directly addresses the unique needs of AI-native clouds in four fundamental ways:
1. Operational agility through disaggregation
The Cisco 8000 Series offers a flexible, open platform ideal for neoclouds seeking rapid innovation. With fully supported Cisco-validated SONiC and key AI features, the platform enables a truly disaggregated stack. This allows for independent hardware and software updates, easy integration of open-source capabilities, and advanced AI observability and traffic engineering. For backend buildouts, the Cisco 8122-64EH-O (64x800G QDD) and 8122-64EHF-O (64x800G OSFP) platforms—both powered by the Cisco Silicon One G200 ASIC—deliver high-performance 800G throughput to meet the needs of demanding AI and data center workloads. These platforms combine reliable, purpose-built hardware with agile, cloud-native software, ensuring a scalable foundation for evolving infrastructure needs.
2. Deterministic, lossless fabric for distributed training
AI clusters depend on synchronized, high-bandwidth, lossless networks to keep thousands of GPUs fully utilized. The Cisco 8122 platforms, built with G200 ASICs, deliver large, fully shared, on-die packet buffer, ultra-low jitter, and adaptive congestion management—all essential for RDMA-based workloads and collective operations. With support for 800G today and 1.6T speeds tomorrow, the fabric can scale as fast as AI ambition grows.
3. Intelligence built in: Advanced AI networking features
Cisco’s offering is anchored by its advanced AI networking features—a rich set of tools designed to provide real-time network insights, workload-aware scheduling, and dynamic congestion isolation. These features enable the fabric to implement predictive traffic steering, aligning network behavior with AI workload patterns to maximize cluster efficiency and throughput.
4. Open, programmable, and future-proof
With open NOS like SONiC, the network becomes as programmable as the AI workloads it supports. Operators can rapidly deploy new features, integrate with GPU schedulers, and extend the telemetry pipeline to match evolving needs. Additionally, the Cisco 8122 platforms are UEC-ready, aligning with the emerging Ultra Ethernet Consortium 1.0 standards to ensure your network is prepared for future AI demands.
Scaling the AI supercloud: Out and across
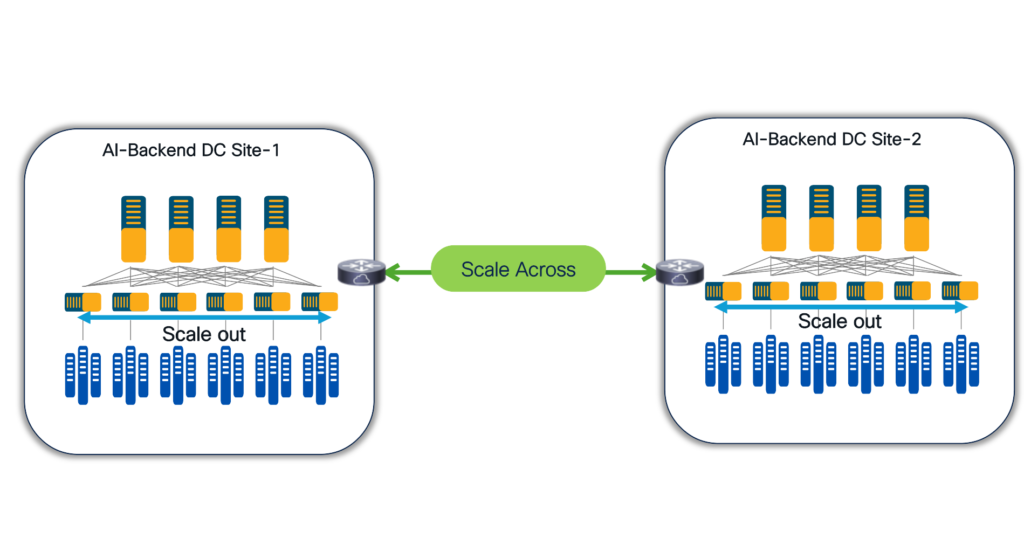

Figure 1: Scale out and scale across
Scale out: Creating multi-tier backend AI fabrics with intelligent fabric capabilities
As AI workloads scale, it is crucial for the underlying network to advance in both bandwidth and intelligence. Cisco multistage Clos topologies, built with Cisco 8122 platforms, deliver truly non-blocking fabrics optimized for large-scale GPU clusters. At the heart of this solution is the comprehensive, AI-native networking feature-set designed to maximize performance and efficiency for AI clusters.
Key capabilities include:
- Advanced congestion management:
Priority Flow Control (PFC) and Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) work in tandem to ensure the highest throughput and minimal latency during congestion, keeping clusters synchronized and running smoothly. - Adaptive routing and switching (ARS):
Dynamically steers traffic according to real-time congestion and flow patterns, maximizing efficiency across the entire network fabric. ARS offers two sub-modes:- Flowlet load balancing: Splits traffic into micro-bursts (flowlets) and routes each along the optimal path, improving utilization while preserving packet order—essential for RDMA-based GPU workloads.
- Packet spraying: Distributes packets across all available paths for maximum throughput, ideal for AI collective operations that tolerate packet reordering.
- Weighted ECMP:
Traffic is distributed unevenly over multiple equal-cost paths according to predefined weights. This ensures higher-capacity or less-congested links carry more traffic, improving overall utilization and performance in large-scale deployments. - QPID hashing:
Employs advanced hashing techniques to evenly spread traffic, minimizing flow collisions and preventing single-path oversubscription. - Packet trimming:
During extreme congestion, non-essential packet payloads are removed to relieve hotspots, while critical header information is retained for continued routing without dropping entire packets. - Flexible topology support:
Compatible with a variety of network architectures—including rail-only, rail-optimized, and traditional leaf/spine topologies. The system supports both IPv4 and IPv6 underlays and integrates with IP/BGP and EVPN-based fabrics, allowing operators to tailor networks to specific AI cluster needs. - Multivendor SmartNIC interoperability:
Designed for seamless integration with a diverse ecosystem of SmartNICs from multiple vendors, ensuring flexibility, investment protection, and future-proof infrastructure. - AI-driven observability with PIE port:
Provides deep, real-time visibility at both per-port and per-flow levels—including GPU-to-GPU traffic and congestion hotspots—using ASIC-level telemetry, in-band INT packet tracing, and SONiC integration. This enables operators to proactively monitor, tune, and troubleshoot networks to optimize AI training outcomes.
Together, these features create a fabric that is not only highly scalable but also truly AI-optimized. The Cisco 8122 platforms’ intelligent networking capabilities enable the network to absorb synchronized traffic bursts, prevent congestion collapse, and keep every GPU operating at peak efficiency—empowering next-generation AI workloads with unmatched performance and reliability.
Scale across: Federating AI pods globally
As AI infrastructure expands beyond single data centers to span regions and continents, scale-across networking becomes critical. Neoclouds need to federate distributed GPU clusters while maintaining the low-latency, high-bandwidth performance that AI workloads demand.
The Cisco 8223, powered by Silicon One P200—the industry’s first 51.2T deep-buffer router—addresses this challenge head-on. With integrated MACsec security, 800GE interfaces supporting both OSFP and QSFP-DD optics, and coherent optics capability, the 8223 delivers the flexibility and efficiency next-generation distributed AI workloads require.
Native SONiC support enables seamless integration between AI backends and WAN connectivity, allowing operators to build open, programmable networks that scale globally without sacrificing the performance characteristics of local clusters.
Accelerating neocloud AI networks with Cisco 8000 Series


Figure 2: Cisco 8000 Series for scale out and scale across
In the AI era, networks have evolved from infrastructure cost centers to competitive differentiators. For neoclouds, networking performance directly impacts GPU utilization, training efficiency, and ultimately, customer success.
By combining the Cisco 8000 Series platforms, advanced AI networking features, and the openness of SONiC, neoclouds can build infrastructure that scales seamlessly, operates efficiently, and adapts as AI workloads evolve. It’s not just about keeping pace with AI innovation—it’s about enabling it.
Additional resources:












